Turritopsis nutricula

Have you ever wondered what would happen if our life cycles were reversed, that is if we were born old and died young? Well, there’s one animal that comes close and has achieved immortality in the process, just to top it off. Meet the Turritopsis nutricula, a small saltwater animal or hydrozoan related to jellyfish and corals.
Like most jellyfish, Turritopsis nutricula undergoes two distinct stages in its life cycle: The polypoid or immature stage, when it’s just a small stalk with feeding tentacles; and the medusa or mature stage when the only 1mm-long polyps asexually produce jellyfish.
Turritopsis nutricula in its aptly named medusa form with a bright red stomach: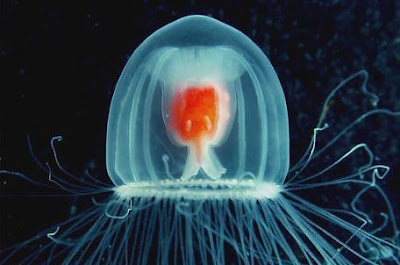
A jellyfish’s lifespan usually ranges from somewhere between a few hours for the smallest species to several months and rarely to a few years for the bigger species. How does the only 4-5 mm long Turritopsis nutricula (let’s call it T’nut) manage to beat the system?
Well, T’nut is able to transform between medusa and polyp stage, thereby reverting back from mature to immature stage and escaping death. The cell process is called transdifferentiation, when non-stem cells either transform into a different type of cell or when an already differentiated or specialised stem cell creates cells outside this specialised path.
The polyp state of Turritopsis rubra, long synonymised with T’nut:

T’nut requires tissue from both the jellyfish bell surface and the circulatory canal system for its transdifferentiation. This switching of cell roles is not unusual and can be seen in many animals and humans, but usually only when parts of an organ regenerate. In T’nut’s case, reverting back to an immature state is part of its regular life cycle.
In its medusa form, Turritopsis nutricula is bell-shaped and about 4-5 mm in diameter. Young specimens will be only 1 mm in diameter and have eight tentacles to start out with but can have between 80 and 90 as adults.
Specimen with a yellow body:

Turritopsis nutricula most likely originated in the Caribbean but can now be found in the temperate to tropical regions in all of the world’s oceans, spreading further through the ballast water that ships discard in ports. According to Dr. Maria Pia Miglietta from the Smithsonian Tropical Marine Institute: “We are looking at a worldwide silent invasion.”
A drawing of various Tuatara species; T’nut is No. 18:

Silent invasion? Possibly, but while Turritopsis nutriculae may be biologically immortal, they are surely not invincible. Especially in their immature stage, they are susceptible to predators and diseases and many die before they even reach jellyfish stage. Still, they are to date the only known animal capable of reverting to an earlier, immature stage.





























































